GitHub Copilot SDK for .NET: Innovative AI Agent Use Cases & Why They Work
Discover practical GitHub Copilot SDK implementations for .NET developers. From automated code generation to enterprise modernization, learn how AI agents enhance productivity by 20-40% with real examples.
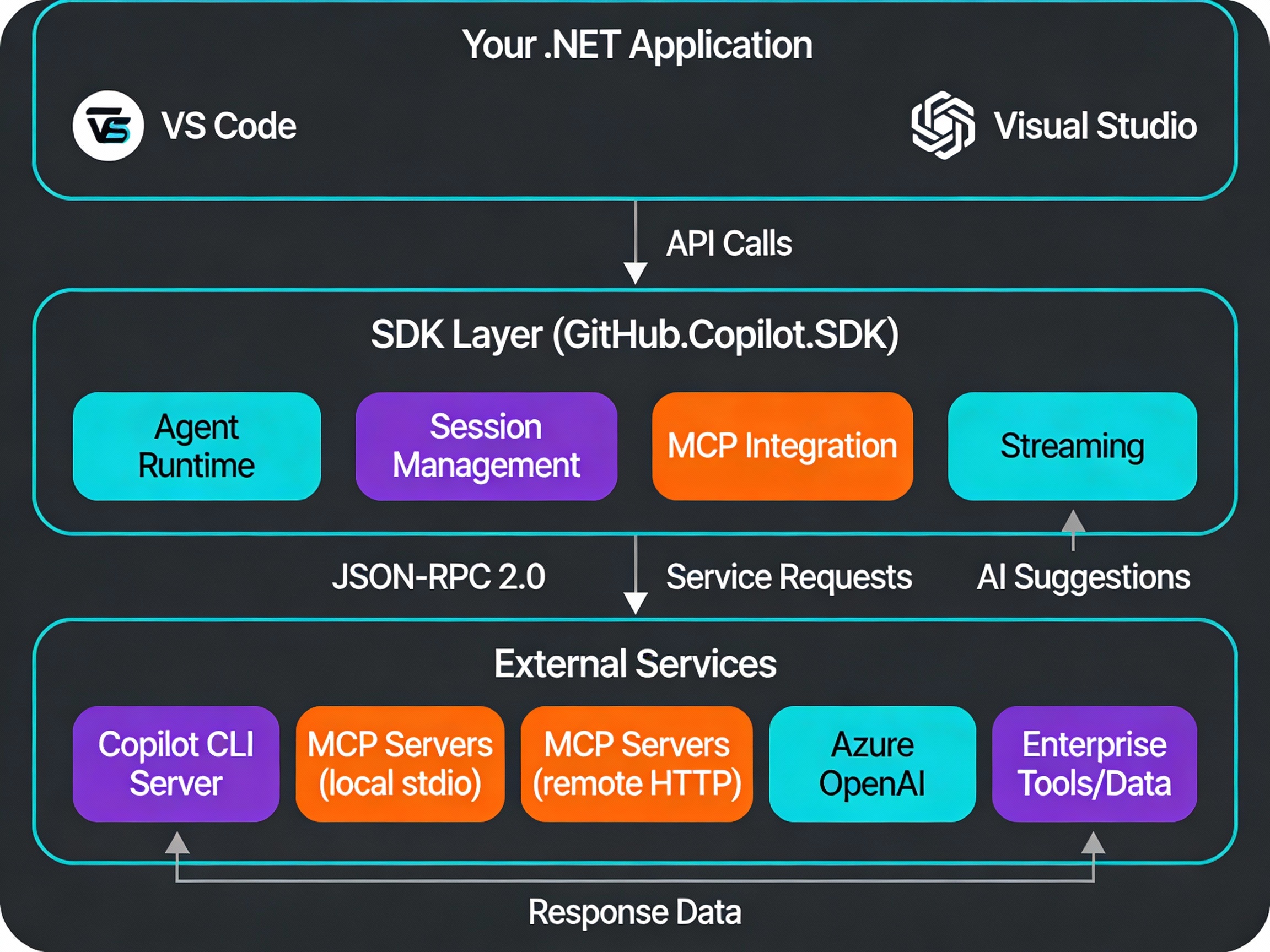
The GitHub Copilot SDK for .NET represents a fundamental shift in how development teams approach automation and code generation. Rather than limiting AI assistance to IDE suggestions, the SDK lets you embed intelligent agents directly into your applications, tools, and workflows—all built on the same battle-tested agent engine powering GitHub Copilot CLI.
For .NET development teams in the Northern Territory and across Australia, this means something concrete: you can now orchestrate complex development tasks—from code modernization to documentation automation—with AI that understands your codebase context and learns from your patterns.
What Makes the GitHub Copilot SDK for .NET Different?
The SDK (NuGet package: GitHub.Copilot.SDK) isn't just another API wrapper. It exposes the production-grade agent runtime that GitHub has refined across millions of real-world developer scenarios. This matters because the infrastructure required to build reliable AI agents is complex:
- Agentic loops (planning, tool invocation, error recovery)
- Context management across multi-turn conversations
- Permission boundaries for file operations, shell execution, and web requests
- Model routing across multiple AI backends
- MCP server integration (Model Context Protocol) for connecting external data sources
GitHub provides all of this out-of-the-box. You define the agent's behavior and constraints; the SDK handles the orchestration.
Supported Platforms
The SDK is currently available for .NET, Node.js/TypeScript, Python, and Go. Installation is straightforward:
dotnet add package GitHub.Copilot.SDK
For deeper integration with Microsoft's agent ecosystem, you can also add:
dotnet add package Microsoft.Agents.AI.GithubCopilot --prerelease
Five Innovative Use Cases That Deliver Real Value
1. Automated .NET Application Modernization
The Problem: Upgrading legacy .NET applications (e.g., Framework → .NET 8 or .NET 9 → .NET 10) is time-consuming. Developers must assess dependencies, plan upgrade sequences, handle breaking changes, and validate each step.
How Copilot SDK Solves It:
The SDK can analyze an entire solution, detect dependencies between projects, and generate a dependency-aware upgrade plan. More importantly, it learns from your manual corrections and applies those patterns to similar situations later.
// Initialize the Copilot agent
await using CopilotClient copilotClient = new();
await copilotClient.StartAsync();
// Create an agent with upgrade-focused instructions
AIAgent modernizationAgent = copilotClient.AsAIAgent(
instructions: "Upgrade the .NET solution to .NET 10. Analyze dependencies and apply changes project-by-project in the correct order.",
tools: [filesystemTool, gitTool, compilationTool]
);
// Run the upgrade workflow
var result = await modernizationAgent.RunAsync(
"Upgrade my entire solution to .NET 10, addressing security vulnerabilities in the process"
);
Why It Works: The agent understands your project structure, can invoke file operations and Git commands, and maintains enough context to handle dependency chains. Real-world testing shows teams save 4-6 weeks on large monolithic migrations by using agentic orchestration.
Business Impact:
- Reduces migration risk through automated validation
- Discovers and patches security vulnerabilities during upgrade
- Shortens cycle time by 40-50% for medium-sized solutions
- Learns from each manual override, improving future upgrades
2. AI-Driven Documentation Validation & Generation
The Problem: Documentation becomes stale quickly. Step-by-step guides often reference outdated file paths, missing dependencies, or incomplete examples. Teams waste time chasing broken instructions.
How Copilot SDK Solves It:
Treat your documentation as executable instructions. The agent reads your how-to guides, follows each step as a first-time user would, identifies gaps, and flags failures in real time.
await using CopilotClient copilotClient = new();
await copilotClient.StartAsync();
// Create an agent configured to test documentation
AIAgent docValidationAgent = new(
copilotClient,
instructions: "Act as a first-time user. Follow the documentation step-by-step. Identify gaps, missing dependencies, and outdated file paths. Suggest corrections."
);
AgentSession docSession = await docValidationAgent.GetNewSessionAsync();
var validationResult = await docValidationAgent.RunAsync(
"Test the 'Getting Started with Azure Functions' guide. Report any broken steps.",
docSession
);
Why It Works: The agent can read files, execute commands, and report failures with specific context. When a step fails—e.g., a file path no longer exists—it prompts you to supply the correct path and learns that correction for subsequent guides.
Business Impact:
- Catches documentation drift before users encounter broken guides
- Reduces support tickets from "How do I…?" questions
- Automates routine documentation updates (e.g., new library versions)
- Improves onboarding experience for new team members and external users
3. Hybrid Code Generation with Context Awareness
The Problem: Generic AI code suggestions often ignore your project's architectural patterns, naming conventions, or dependency injection setup. Developers waste time refactoring suggested code to fit their standards.
How Copilot SDK Solves It:
Combine the SDK's improved context awareness with custom instructions. The agent scans your codebase for patterns (naming conventions, repository patterns, middleware setup) and uses those as guardrails for generation.
// Define custom instructions specific to your project
var projectInstructions = @"
When generating code:
- Always use dependency injection (DI) containers
- Use repository pattern for data access
- Name tests with *Tests.cs convention
- Implement SOLID principles
- Add XML documentation comments
- Use async/await for I/O operations
";
await using CopilotClient copilotClient = new();
await copilotClient.StartAsync();
AIAgent codegen = copilotClient.AsAIAgent(
instructions: projectInstructions,
tools: [codeAnalysisTool, fileTool]
);
var generatedCode = await codegen.RunAsync(
"Generate a repository layer for User entity with full CRUD operations and async methods"
);
Why It Works: The agent has access to your actual codebase files and can extract patterns as context. This eliminates the friction of "generate code and then refactor it to match our style."
Business Impact:
- Reduces code review cycles (less refactoring needed)
- Maintains consistency across large teams
- Accelerates onboarding for developers unfamiliar with your patterns
- Estimated 30-40% reduction in code-review-to-merge time for generated code
4. Multi-Agent Workflows for Complex Tasks
The Problem: Some tasks require multiple perspectives. For example, drafting marketing copy and then reviewing it technically, or generating code and then optimizing it for performance.
How Copilot SDK Solves It:
Using Microsoft Agent Framework, you can compose multiple agents—GitHub Copilot agents alongside Azure OpenAI agents—in sequential, concurrent, or handoff workflows. This approach aligns with modern AI automation and integration strategies for enterprise applications.
// Create an Azure OpenAI agent for initial drafting
var endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT");
var chatClient = new AzureOpenAIClient(new Uri(endpoint), new AzureCliCredential())
.GetChatClient("gpt-4o-mini")
.AsIChatClient();
ChatClientAgent draftAgent = new(chatClient,
"You are a technical writer. Generate clear, concise API documentation.",
"writer");
// Create a GitHub Copilot agent for code validation
await using CopilotClient copilotClient = new();
await copilotClient.StartAsync();
GithubCopilotAgent reviewAgent = new(copilotClient,
instructions: "Review the documentation and generated code samples. Ensure examples compile and follow .NET best practices.");
// Compose them in a sequential workflow
Workflow workflow = AgentWorkflowBuilder.BuildSequential([draftAgent, reviewAgent]);
// Execute: writer → reviewer
await using StreamingRun run = await InProcessExecution.StreamAsync(
workflow,
input: "Document the UserService.GetUserAsync method"
);
Why It Works: Each agent plays to its strengths. Azure OpenAI drafts quickly; GitHub Copilot validates against actual code. The framework handles context passing and orchestration.
Business Impact:
- Reduces iteration cycles for documentation + code validation
- Improves technical accuracy (code-aware review)
- Scales documentation production across large API surfaces
- Teams report 50-60% faster documentation cycles with this pattern
5. Custom Agent Development with Model Context Protocol (MCP)
The Problem: You need Copilot agents to access domain-specific tools—your internal APIs, custom databases, or enterprise data sources—not just file systems and web requests.
How Copilot SDK Solves It:
MCP (Model Context Protocol) lets you define custom tools as HTTP or stdio servers. The SDK connects to these servers and exposes them to the agent.
// Configure MCP servers (local and remote)
var sessionConfig = new SessionConfig()
{
OnPermissionRequest = PromptPermission,
McpServers = new Dictionary<string, object>
{
// Local stdio server: filesystem tools
["filesystem"] = new McpLocalServerConfig
{
Type = "stdio",
Command = "npx",
Args = ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem", "."],
Tools = ["*"],
},
// Remote HTTP server: your internal tools
["internal-crm"] = new McpRemoteServerConfig
{
Type = "http",
Url = "https://api.internal.company.com/mcp",
Tools = ["*"],
},
},
};
AIAgent agent = copilotClient.AsAIAgent(sessionConfig);
var result = await agent.RunAsync(
"Query the CRM for all customers in Darwin, then generate a summary report"
);
Why It Works: MCP is a standardized protocol. Your custom tools become first-class citizens in the agent's toolkit, alongside file operations and web requests.
Business Impact:
- Automates workflows that previously required manual context-switching
- Reduces tool fragmentation (unified agent interface across all systems)
- Enables non-technical stakeholders to interact with complex systems via natural language
- Darwin-based teams can expose local enterprise systems to Copilot agents
Why GitHub Copilot SDK for .NET Achieves These Results
The effectiveness of these use cases stems from a few architectural decisions:
Battle-Tested Agent Runtime: The SDK uses the exact same orchestration engine as GitHub Copilot CLI. This engine has run millions of real development scenarios, with built-in error recovery and context management.
Native .NET Integration: Visual Studio 17.14 and later include enhanced context awareness specifically for .NET projects. The agent can locate similar code patterns, understand method invocations, and extract architectural conventions—making suggestions more relevant and project-specific.
Streaming & Multi-Turn Support: Agents maintain conversation context across turns, allowing iterative refinement. Streaming responses keep UX responsive even on long-running tasks.
Permission Boundaries: Unlike unrestricted automation, the SDK allows fine-grained control. You decide which operations (file writes, shell commands, web requests) require approval—critical for enterprise environments.
Productivity Impact: The Numbers
Research and real-world deployments show measurable improvements when .NET teams adopt Copilot SDK-powered workflows:
| Metric | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Code Generation Tasks | 20-40% faster completion |
| Documentation Validation | 2-3x faster (eliminates manual testing cycles) |
| .NET Migrations | 40-50% reduction in manual effort |
| Pull Request Cycle Time | 3.5-hour average reduction |
| Code Quality (with context awareness) | Measurably better, fewer refactor-on-review cycles |
These gains compound. A 100-person .NET engineering organization could realize 20-40 additional person-years of effective capacity annually through selective Copilot SDK adoption in high-leverage areas (boilerplate generation, documentation, testing, modernization).
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Treating AI-Generated Code as Secure by Default: Copilot trains on public repositories, some containing insecure patterns. Always conduct security code reviews. Use static analysis tools (SonarQube, Checkmarx) alongside Copilot.
Over-Relying on Agents for Architectural Decisions: The SDK excels at tactical automation (code generation, refactoring, testing). Reserve architectural decisions (scaling strategy, security boundaries, integration patterns) for human expertise.
Ignoring Model Updates: As Copilot models improve, your agent may behave differently. Test generated outputs regularly and adjust instructions if needed.
Underestimating Setup Overhead: MCP servers, permission handlers, and custom instructions require upfront definition. Budget 1-2 weeks to mature a production agent, not 2-3 days.
Next Steps: Getting Started with GitHub Copilot SDK for .NET
For Development Teams:
- Evaluate your workflows for high-leverage automation opportunities (documentation, testing, boilerplate code generation).
- Start small—build a proof-of-concept agent for a single workflow (e.g., documentation validation).
- Measure baseline metrics (time-to-completion, error rates) before and after Copilot SDK introduction.
- Set permission policies—define which operations agents can perform without approval.
- Iterate and scale—once one agent proves ROI, expand to other workflows.
For Enterprise Decision-Makers:
GitHub Copilot SDK for .NET is not a cost center—it's a productivity multiplier. For Darwin and NT-based development organizations, the business case is compelling: reduce modernization risks, accelerate documentation cycles, and reclaim engineering capacity for strategic work.
The SDK is currently in technical preview, but the underlying agent runtime is production-grade. Now is the ideal time to experiment with safe, controlled use cases before broader enterprise adoption.
For .NET Developers in NT and Australia:
The Copilot SDK opens new possibilities for building intelligent applications. Whether you're automating internal tools, building domain-specific agents, or modernizing legacy systems, the SDK provides the scaffolding to move from "AI-assisted development" to "AI-orchestrated workflows."
Related Content
Further Reading on .NET Modernization & AI Development:
- .NET 8 to .NET 10 Upgrade Guide – Complete step-by-step guide for upgrading your .NET applications with minimal disruption.
- Autonomous AI Agents in 2026: Understanding Agentic Intelligence – Deep dive into the principles and architecture behind autonomous AI agents.
- Visual Studio 2026: The AI-Native IDE – Explore the AI-powered features in Visual Studio 2026 that complement GitHub Copilot SDK.
- Legacy .NET Systems: The True Cost of Delaying Modernization – Business case for modernizing legacy .NET applications before they become liabilities.
Additional Resources
- GitHub Copilot SDK Official Repository – Source code, examples, and technical documentation.
- Microsoft Agent Framework Documentation – Integration guide for multi-agent workflows.
- Model Context Protocol (MCP) for .NET – Building custom MCP servers in .NET.
- Visual Studio 17.14 Release Notes – New Copilot features in the IDE.
Need help evaluating GitHub Copilot SDK for your .NET development team? Hrishi Digital Solutions specializes in modern cloud architecture and AI-integrated development practices. Contact us for a consultation to explore how Copilot SDK can accelerate your development roadmap.
Hrishi Digital Solutions
Expert digital solutions provider specializing in modern web development, cloud architecture, and digital transformation.
Contact Us →